Search Result
Results for "
dioxide
" in MedChemExpress (MCE) Product Catalog:
9
Biochemical Assay Reagents
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Areas |
Chemical Structure |
-
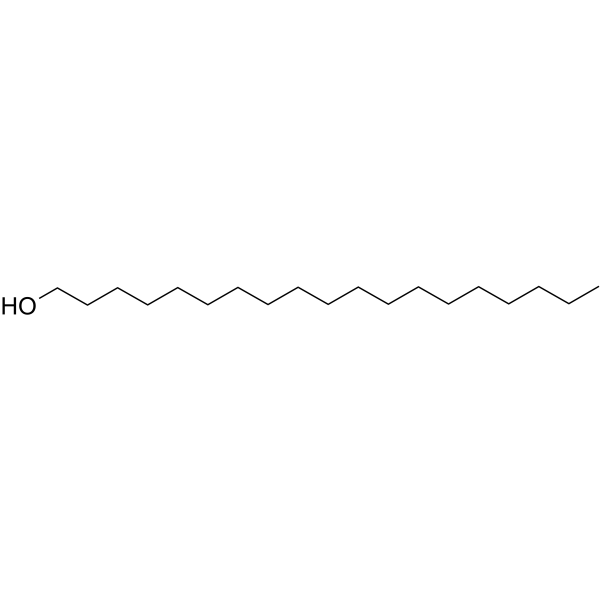
- HY-W004297
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
1-Nonadecanol is one of the compositions of supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) essential oil of Heracleum thomsonii. 1-Nonadecanol is also an important aroma compound in Neotinea ustulata .
|
-
-
- HY-E70015
-
|
PEPC
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, Microorganism (PEPC) is a carbon dioxide fixing enzyme that in an irreversible manner and in the presence of Mg 2+, converts phosphoenolpyruvate and bicarbonate into oxaloacetate and inorganic phosphorus. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase catalyses the primary assimilation of CO(2) in Crassulacean acid metabolism plants. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase plays a major role in setting the day-night pattern of metabolism in plants .
|
-
-
- HY-W051271
-
|
Titanium dioxide
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Titanium(IV) oxide is a photosensitizer. Titanium(IV) oxide can be used as an excipient, such as glidant, coating agent, opacifier, coloring agent. Pharmaceutical excipients, or pharmaceutical auxiliaries, refer to other chemical substances used in the pharmaceutical process other than pharmaceutical ingredients. Pharmaceutical excipients generally refer to inactive ingredients in pharmaceutical preparations, which can improve the stability, solubility and processability of pharmaceutical preparations. Pharmaceutical excipients also affect the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) processes of co-administered drugs .
|
-

-
- HY-128974
-
|
Lauryl Maltoside
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
N-Dodecyl-β-D-maltoside (Lauryl Maltoside) is a non-ionic detergent. N-Dodecyl-β-D-maltoside has strong adsorption on alumina, titanium dioxide and hematite. N-Dodecyl-β-D-maltoside can promote the reactivation of various proteins. N-Dodecyl-β-D-maltoside can effectively stabilize photoactive reaction center complexes (RCs) and inhibit the degradation of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides R-26 reaction center in solution. N-Dodecyl-β-D-maltoside can be used for purification and stabilization of RNA polymerase and for detection of protein-lipid interactions .
|
-
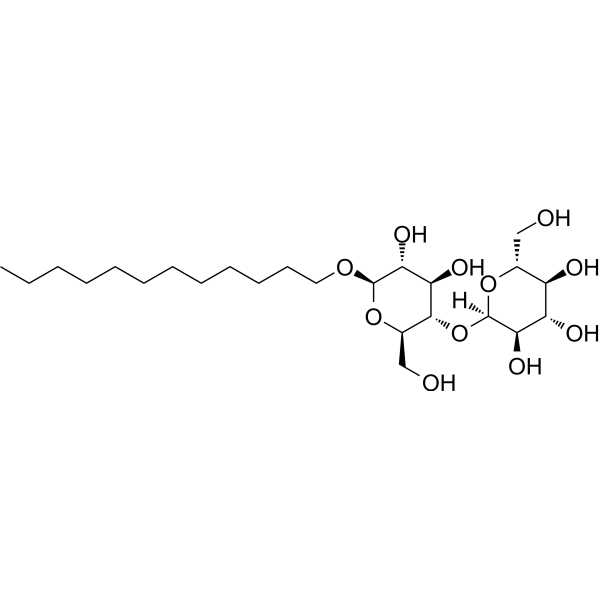
-
- HY-131164
-
|
|
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
Potassium clavulanate mixture with silicon dioxide (1:1) is a powdered mixture of 1 part Potassium clavulanate to 1 part Silicon dioxide .
|
-
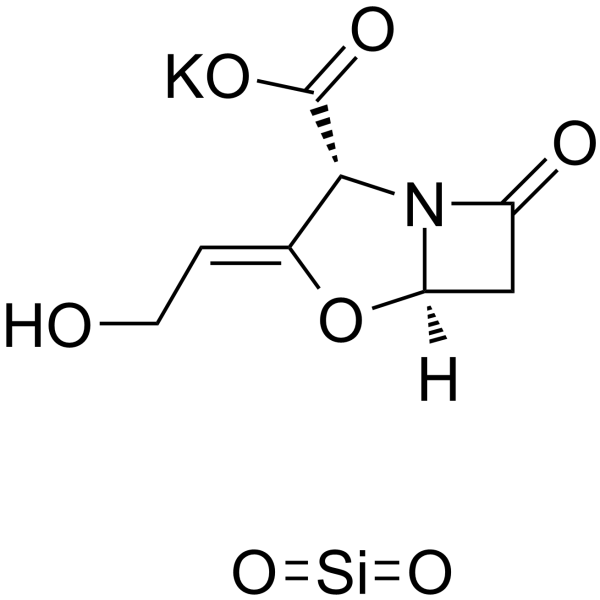
-
- HY-116772
-
|
Irganox 1790
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
Cyanox CY 1790 (Irganox 1790) is an antioxidant with chlorine dioxide resistance .
|
-

-
- HY-10704
-
|
PTP1B inhibitor
|
Phosphatase
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
PTP1B-IN-1 is a potent protein tyrosine phosphatase-1B (PTP1B) inhibitor with IC50 of 1.6 mM; 1,2,5-thiadiazolidin-3-one-1,1-dioxide scaffold for derivatives synthesis.
|
-
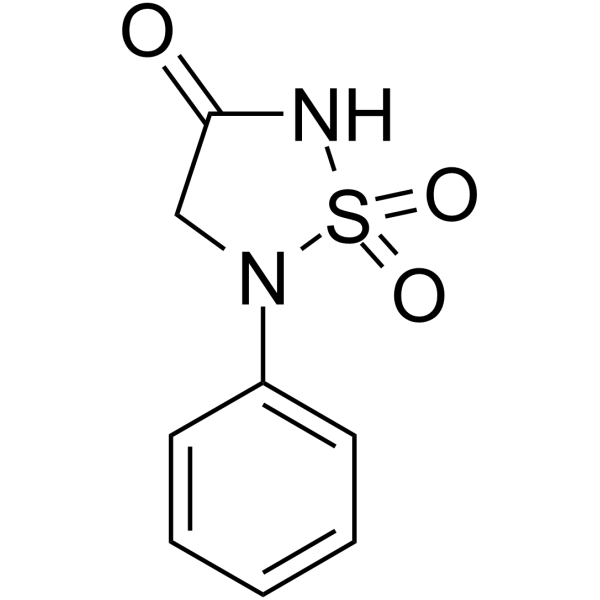
-
- HY-133603
-
|
|
Others
|
Others
|
|
4,5-Dichloroveratrole is a chlorinated product formed by reaction of Veratryl alcohol (VE; HY-107858) with chlorine dioxide solution .
|
-
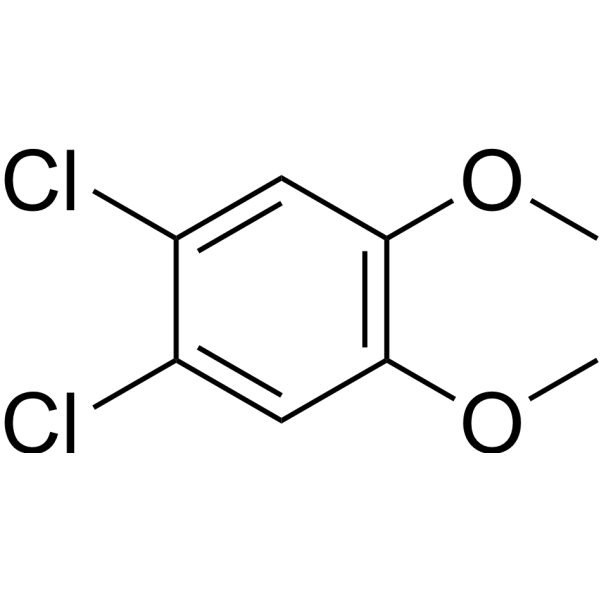
-
- HY-W013767
-
|
|
Others
|
Infection
|
|
Thiodicarb is a carbamate insecticide used to control flies in animal and poultry houses and dairies. Thiodicarb is metabolized into methomyl in animals and plants, and subsequently degraded into carbon dioxide and acetonitrile .
|
-
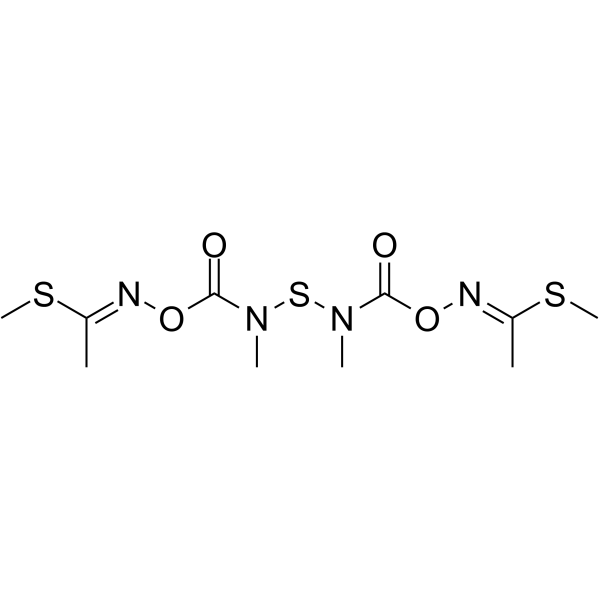
-
- HY-P2767
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Others
|
|
Urease, Jack bean is derived from jack bean and Catalyzes hydrolysis of urea to carbon dioxide and ammonia. Urease, Jack bean is useful in the determination of urea in body fluids.
|
-

-
- HY-149975
-
|
|
iGluR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
AMPA receptor modulator-4, a 3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide (BTD), is an orally active positive allosteric modulator of the AMPA receptors (AMPAR PAMs). AMPA receptor modulator-4 can cross the blood-brain barrier. AMPA receptor modulator-4 increases the cognition performance and improves working memory performance in mice .
|
-
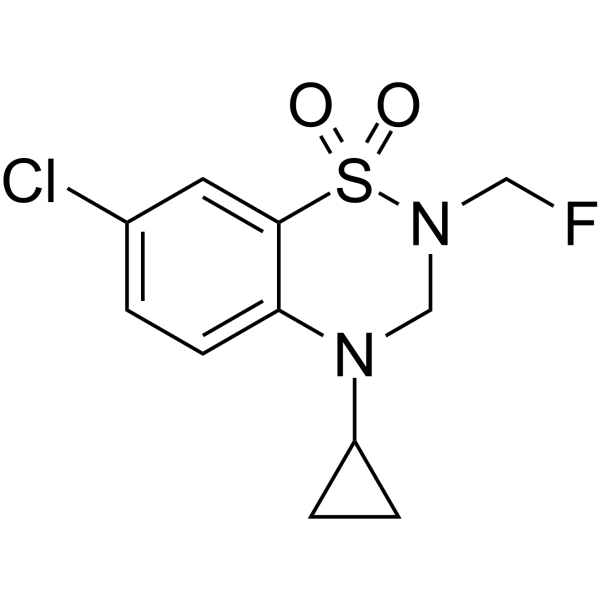
-
- HY-B2205
-
|
Activated magnesium silicate
|
Fungal
|
Infection
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Magnesium silicate (Activated magnesium silicate) is a compound of magnesium oxide (MgO) and silicon dioxide (SiO2). Magnesium silicate is used in antiacid and antiulcer preparation, and as a deodorizer, decolorizer and antifungal .
|
-
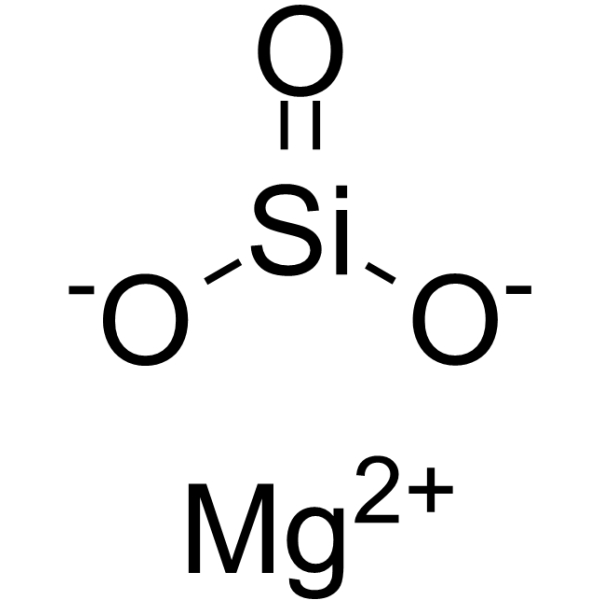
-
- HY-D0227
-
|
Tris; Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
|
THAM (Tris) is a biologically inert amino alcohol of low toxicity, which buffers carbon dioxide and acids in vitro and in vivo. THAM is an effective amine compound for pH control in the physiological range .
|
-
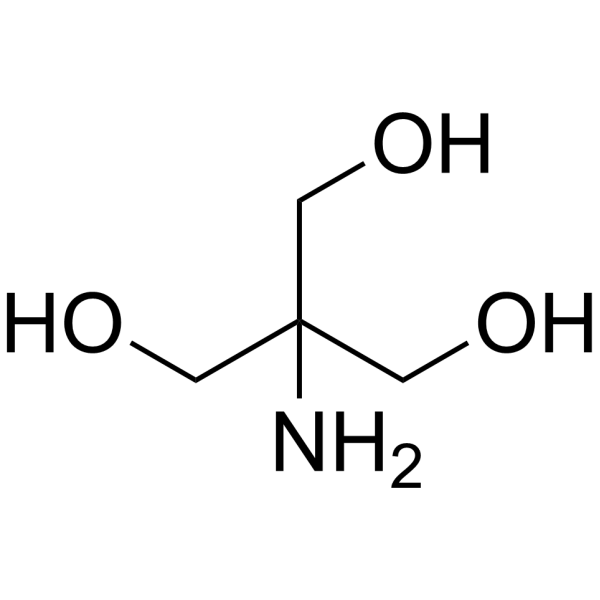
-
- HY-D0227B
-
|
Tris acetate; Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane acetate
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Trometamol acetate (Tromethamine acetate) is a biologically inert amino alcohol of low toxicity, which buffers carbon dioxide and acids in vitro and in vivo. Trometamol acetate is an effective amine compound for pH control in the physiological range .
|
-
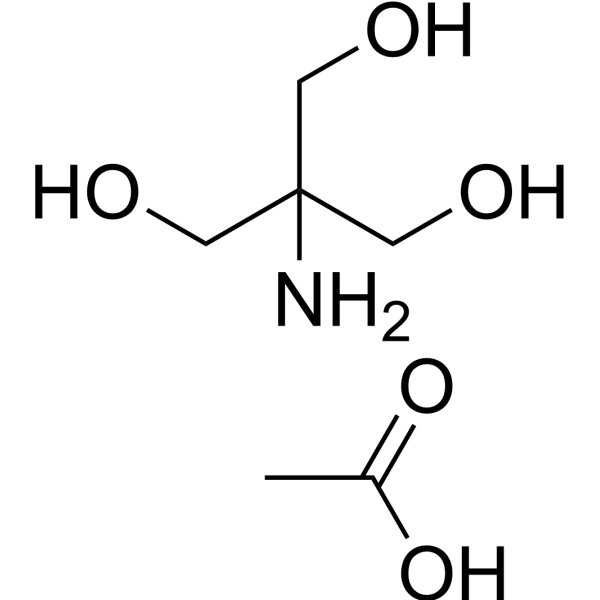
-
- HY-D0227A
-
|
Tris HCl; Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane hydrochloride
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
|
THAM hydrochloride (Tris HCl) is a biologically inert amino alcohol of low toxicity, which buffers carbon dioxide and acids in vitro and in vivo. THAM hydrochloride is an effective amine compound for pH control in the physiological range .
|
-
-
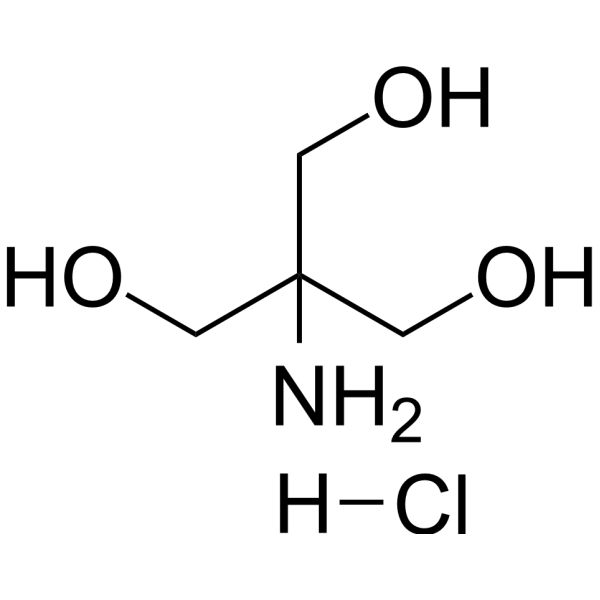
- HY-P2891
-
|
PoxB
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
Pyruvate Oxidase, Microorganisms (PoxB) is a thiamine pyrophosphate-dependent oxidase that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl phosphate, carbon dioxide and water. Pyruvate oxidase is an important enzyme in bacterial metabolism and is often used in biochemical research .
|
-

-
- HY-P2825
-
|
TDC; TyrDC
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Tyrosine decarboxylase, Microorganism (TDC) widely exists in plants, insects and different microorganisms, and is often used in biochemical research. Tyrosine decarboxylase is a pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP)-dependent decarboxylase that catalyzes the removal of carboxyl groups from tyrosine to produce tyramine and carbon dioxide .
|
-
-
- HY-P2907
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
Formate dehydrogenase is an enzyme ubiquitous in prokaryotes and eukaryotes that catalyzes the reversible oxidation of formate to carbon dioxide. According to its metal content, structure and catalytic strategy, Formate dehydrogenase can be divided into two categories, non-metallic and metal-containing, which are often used in biochemical research .
|
-

-
- HY-P2995
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Hemoglobin is a iron-containing protein in red blood cells with oxygen binding properties. Hemoglobin consits of heme, which binds to oxygen. Hemoglobin also transports other gases, such as carbon dioxide, nitric oxide, hydrogen sulfide and sulfide. Hemoglobin absorbs unneeded oxygen in tissues, as an antioxidant .
|
-
-
- HY-19698
-
|
4-CPA; p-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid (4-CPA) is a widely used herbicide for weed control in agriculture. 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid can be degraded in aqueous media through an electrochemical oxidation process. The end products of 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid degradation are harmless, such as carbon dioxide, water, and chloride ions .
|
-

-
- HY-D0227AR
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
|
THAM (hydrochloride) (Standard) is the analytical standard of THAM (hydrochloride). This product is intended for research and analytical applications. THAM hydrochloride (Tris HCl) is a biologically inert amino alcohol of low toxicity, which buffers carbon dioxide and acids in vitro and in vivo. THAM hydrochloride is an effective amine compound for pH control in the physiological range .
|
-

-
- HY-P1775
-
|
EC 4.2.1.1
|
Carbonic Anhydrase
|
Neurological Disease
Metabolic Disease
Cancer
|
Carbonic anhydrase, Bovine erythrocytes (EC 4.2.1.1) is ubiquitous zinc-containing metalloenzyme present in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Carbonic anhydrase can catalyze reversible conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate and protons. Carbonic anhydrase can be used for the research of cancer, glaucoma, obesity and epilepsy .
|
-
-
- HY-133073
-
|
CCR7-Cmp2105
|
CCR
Ligands for Target Protein for PROTAC
|
Cancer
|
|
CCR7 Ligand 1 (CCR7-Cmp2105) is an allosteric Ligand and antagonist for human CC chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7) with a Kd of 3 nM. CCR7 Ligand 1, thiadiazole-dioxide ligan, suppresses arrestin binding in response to activation by CCL19 with an IC50 of 7.3 μM .
|
-
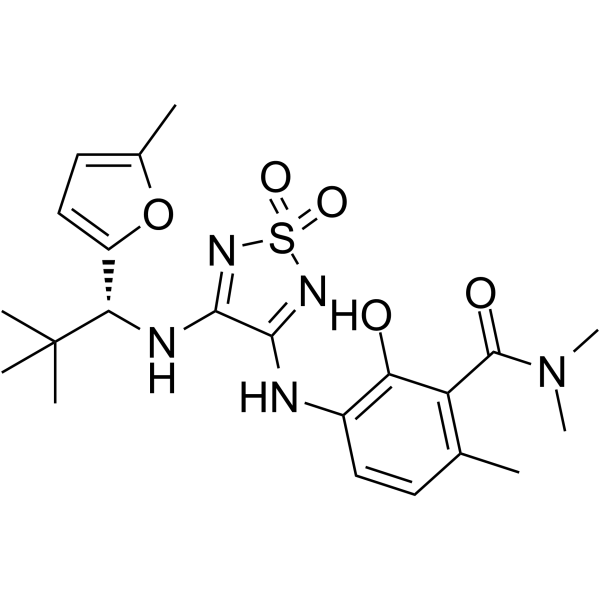
-
- HY-W127787
-
|
L-(+)-Tartaric acid sodium hydrate
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
L-Tartaric acid (L-(+)-Tartaric acid) sodium hydrate is the enantiomer of D-tartaric acid. L-Tartaric acid (HY-Y0293) is a white crystalline dicarboxylic acid found in many plants, such as grapes, and is one of the main organic acids in wine. L-Tartaric acid sodium hydrate which acts as a flour bulking agent and as a food additive can interact with sodium bicarbonate to produce carbon dioxide .
|
-
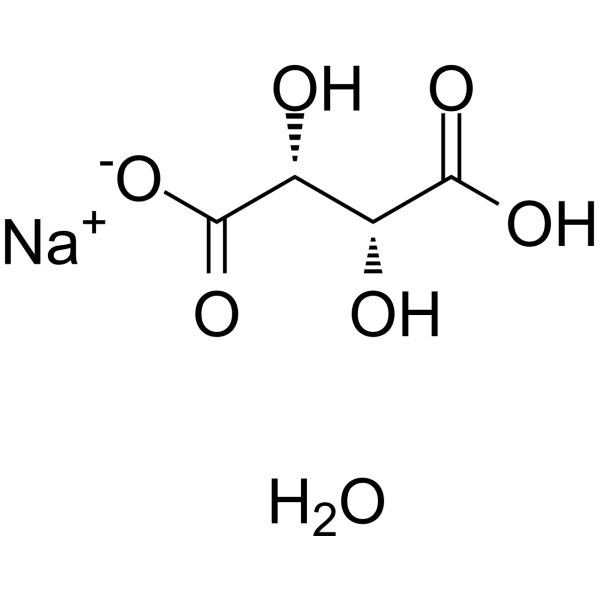
-
- HY-155887
-
|
DSPE-PEG-NH2, MW 3400 ammonium
|
Liposome
|
Others
|
|
DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 3400 (ammonium) is a phosphoethanolamine involved in the synthesis of liposomes for delivery systems. The amino group of DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 3400 (ammonium) can be converted to aromatic aldehydes by reacting with acetone-protected aromatic hydrazines on the surface of bovine carbonic anhydrase (BCA) molecules. Liposomes form a liposome-BAH-BCA conjugate by forming a bisarylhydrazone (BAH) with the target enzyme molecule. The conjugate catalyzes the hydration of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate.
|
-

-
- HY-155908
-
|
DSPE-PEG-NH2, MW 10000 ammonium
|
Liposome
|
Others
|
|
DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 10000 (ammonium) is a phosphoethanolamine involved in the synthesis of liposomes for delivery systems. The amino group of DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 10000 (ammonium) can be converted into aromatic aldehydes by reacting with acetone-protected aromatic hydrazines on the surface of bovine carbonic anhydrase (BCA) molecules. Liposomes form a liposome-BAH-BCA conjugate by forming a bisarylhydrazone (BAH) with the target enzyme molecule. The conjugate catalyzes the hydration of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate.
|
-

-
- HY-Y0698
-
|
Acetothioamide; TAA; Thiacetamide
|
Necroptosis
|
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Thioacetamide (TAA) is an indirect hepatotoxin and causes parenchymal cell necrosis. Thioacetamide requires metabolic activation by microsomal CYP2E1 to thioacetamide-S-oxide initially and then to thioacetamide-S-dioxide, which is a highly reactive metabolite, and its reactive metabolites covalently bind to proteins and lipids thereby causing oxidative stress and centrilobular necrosis. Thioacetamide can induce chronic liver fibrosis, encephalopathy and other events model .
|
-
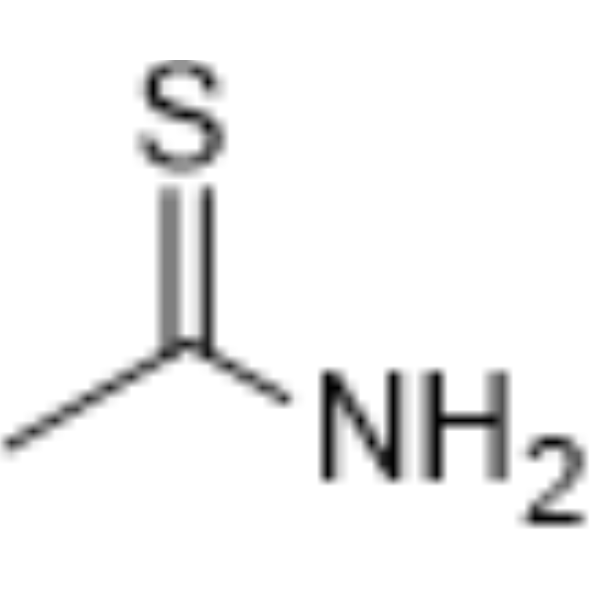
-
- HY-155907
-
|
DSPE-PEG-NH2, MW 5000 ammonium
|
Liposome
|
Others
|
|
DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 5000 (ammonium) is a phosphoethanolamine involved in the synthesis of liposomes for delivery systems. DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 5000 (ammonium) amino group can be converted to aromatic aldehydes that react with acetone-protected aromatic hydrazides on the surface of the bovine carbonic anhydrase (BCA) molecule. Liposomes produce liposome-Bah-BCA conjugates by forming diaryl hydrazone (BAH) with target enzyme molecules. The conjugate catalyzes the hydration of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate.
|
-

-
- HY-W440823A
-
|
DSPE-PEG-NH2, MW 1000 ammonium
|
Liposome
|
Others
|
|
DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 1000 (ammonium) is a phosphoethanolamine involved in the synthesis of liposomes for delivery systems. The amino group of DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 1000 (ammonium) can be converted to an aromatic aldehyde, which reacts with an acetone-protected aromatic hydrazine on the surface of the bovine carbonic anhydrase (BCA) molecule. Liposomes form a liposome-BAH-BCA conjugate by forming a bisarylhydrazone (BAH) with the target enzyme molecule. The conjugate catalyzes the hydration of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate.
|
-

| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
-
- HY-W015915
-
|
Thiourea dioxide
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Aminoiminomethanesulphinic acid (Thiourea dioxide) is a biological material or organic compound that can be used in life science research .
|
-
- HY-P2995
-
|
|
Native Proteins
|
|
Hemoglobin is a iron-containing protein in red blood cells with oxygen binding properties. Hemoglobin consits of heme, which binds to oxygen. Hemoglobin also transports other gases, such as carbon dioxide, nitric oxide, hydrogen sulfide and sulfide. Hemoglobin absorbs unneeded oxygen in tissues, as an antioxidant .
|
-
- HY-19698
-
|
4-CPA; p-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid (4-CPA) is a widely used herbicide for weed control in agriculture. 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid can be degraded in aqueous media through an electrochemical oxidation process. The end products of 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid degradation are harmless, such as carbon dioxide, water, and chloride ions .
|
-
- HY-W127787
-
|
L-(+)-Tartaric acid sodium hydrate
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
L-Tartaric acid (L-(+)-Tartaric acid) sodium hydrate is the enantiomer of D-tartaric acid. L-Tartaric acid (HY-Y0293) is a white crystalline dicarboxylic acid found in many plants, such as grapes, and is one of the main organic acids in wine. L-Tartaric acid sodium hydrate which acts as a flour bulking agent and as a food additive can interact with sodium bicarbonate to produce carbon dioxide .
|
-
- HY-P2907
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Formate dehydrogenase is an enzyme ubiquitous in prokaryotes and eukaryotes that catalyzes the reversible oxidation of formate to carbon dioxide. According to its metal content, structure and catalytic strategy, Formate dehydrogenase can be divided into two categories, non-metallic and metal-containing, which are often used in biochemical research .
|
-
- HY-155887
-
|
DSPE-PEG-NH2, MW 3400 ammonium
|
Drug Delivery
|
|
DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 3400 (ammonium) is a phosphoethanolamine involved in the synthesis of liposomes for delivery systems. The amino group of DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 3400 (ammonium) can be converted to aromatic aldehydes by reacting with acetone-protected aromatic hydrazines on the surface of bovine carbonic anhydrase (BCA) molecules. Liposomes form a liposome-BAH-BCA conjugate by forming a bisarylhydrazone (BAH) with the target enzyme molecule. The conjugate catalyzes the hydration of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate.
|
-
- HY-155908
-
|
DSPE-PEG-NH2, MW 10000 ammonium
|
Drug Delivery
|
|
DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 10000 (ammonium) is a phosphoethanolamine involved in the synthesis of liposomes for delivery systems. The amino group of DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 10000 (ammonium) can be converted into aromatic aldehydes by reacting with acetone-protected aromatic hydrazines on the surface of bovine carbonic anhydrase (BCA) molecules. Liposomes form a liposome-BAH-BCA conjugate by forming a bisarylhydrazone (BAH) with the target enzyme molecule. The conjugate catalyzes the hydration of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate.
|
-
- HY-155907
-
|
DSPE-PEG-NH2, MW 5000 ammonium
|
Drug Delivery
|
|
DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 5000 (ammonium) is a phosphoethanolamine involved in the synthesis of liposomes for delivery systems. DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 5000 (ammonium) amino group can be converted to aromatic aldehydes that react with acetone-protected aromatic hydrazides on the surface of the bovine carbonic anhydrase (BCA) molecule. Liposomes produce liposome-Bah-BCA conjugates by forming diaryl hydrazone (BAH) with target enzyme molecules. The conjugate catalyzes the hydration of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate.
|
-
- HY-W440823A
-
|
DSPE-PEG-NH2, MW 1000 ammonium
|
Drug Delivery
|
|
DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 1000 (ammonium) is a phosphoethanolamine involved in the synthesis of liposomes for delivery systems. The amino group of DSPE-PEG-Amine, MW 1000 (ammonium) can be converted to an aromatic aldehyde, which reacts with an acetone-protected aromatic hydrazine on the surface of the bovine carbonic anhydrase (BCA) molecule. Liposomes form a liposome-BAH-BCA conjugate by forming a bisarylhydrazone (BAH) with the target enzyme molecule. The conjugate catalyzes the hydration of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate.
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Category |
Target |
Chemical Structure |
Your information is safe with us. * Required Fields.
Inquiry Information
- Product Name:
- Cat. No.:
- Quantity:
- MCE Japan Authorized Agent: